Table of Contents
Water loss from aging pipelines isn't just a maintenance headache; it is a multi-billion dollar global crisis. Municipalities and industrial contractors are constantly battling the limitations of traditional materials like concrete, steel, and PVC—fighting a losing war against catastrophic leaks, corrosion, and ballooning maintenance budgets. As a procurement officer or civil engineer, you know that choosing the right material isn't just about the initial invoice; it is about securing the asset for the long haul. The HDPE water pipe stands as the definitive engineering answer to these systemic failures, offering a service life that frequently clears the century mark.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is no longer just an alternative; it is the gold standard for resilient, modern water infrastructure. Unlike rigid materials that crack when the ground shifts or corrode in aggressive soil, HDPE provides a fused, monolithic system that virtually eradicates water loss. This article takes a technical deep-dive into the six core advantages of HDPE piping, backed by ASTM standards and comparative data, to help you make data-driven specification decisions for your next major water supply project.

HDPE 101: Material Science and Core Properties
Molecular Structure and Tensile Strength
To appreciate HDPE’s superior performance, you must first look at its molecular architecture. HDPE is defined by linear polymer chains with very little branching. This linearity allows the molecules to pack tightly together, creating a high-density matrix (0.941 – 0.965 g/cm³). For the engineer, this density translates directly into exceptional tensile strength and flexibility.
Unlike amorphous polymers, HDPE’s semi-crystalline nature strikes a unique balance between stiffness and toughness. It exhibits high tensile strength at yield (typically 26-33 MPa), enabling it to handle significant internal pressure. Moreover, its ductility is proven by tensile strain capabilities exceeding 200% at ultimate failure. Simply put, the pipe can deform significantly under stress without rupturing—a vital safety factor for buried infrastructure.
Critical Material Standards and Property Minimums
Sourcing high-quality HDPE water pipe demands strict adherence to international material standards. The resin used in manufacturing must hit specific cell classifications found in ASTM D3350 or ISO 4427. For example, a standard specification like PE 345464C guarantees the resin meets rigorous criteria for density, melt index, flexural modulus, and tensile strength.
These aren't just bureaucratic checkboxes; they are your performance baseline. ISO 4427 specifically governs polyethylene pipes for water supply, dictating that the raw material must remain stable during extrusion and throughout its service life. When you source from an OEM factory, verifying compliance with these specific ASTM and ISO resin standards is step one in quality assurance, ensuring the final product performs exactly as your hydraulic models predict.
PE80 vs. PE100 vs. PE100RC: Grading the Material
Polyethylene resins have evolved into distinct grades, primarily PE80, PE100, and PE100-RC (Resistant to Crack). While PE80 was the go-to for decades, PE100 has largely replaced it thanks to a higher Minimum Required Strength (MRS). PE100 boasts a superior elastic modulus and strain hardening modulus. This allows for thinner wall sections (higher SDR) to achieve the same pressure rating, saving on material costs while boosting flow capacity.
The most advanced grade, PE100-RC, tackles the specific issue of slow crack growth (SCG). While it maintains the same MRS as standard PE100, the RC grade is engineered to resist point loading failures caused by rocks or bedding irregularities. This makes PE100-RC the smart choice for trenchless methods like Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) or sand-less bedding installations, where the pipe exterior faces harsh physical abrasion.
Weatherability: The Role of Carbon Black
There is a persistent myth that sunlight destroys plastic pipes. However, HDPE water pipes are formulated specifically to fight UV degradation. The material compound typically includes 2-3% finely dispersed carbon black. This additive acts as a powerful UV absorber, intercepting ultraviolet radiation and converting it to heat, preventing the polymer chains from breaking down.
This stabilization means HDPE pipes can be stored outdoors or used in above-ground applications for years without compromising their pressure rating or mechanics. The dispersion of carbon black is key; ASTM D1603 testing ensures the content is uniform throughout the pipe wall. This inherent weatherability gives HDPE a massive edge over materials like PVC, which often need painting or shielding to stop them from becoming brittle in the sun.

HDPE pipe resin pellets and cross-section material detail
Core Advantage 1: Unmatched Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Resistance to Aggressive Environments
Corrosion kills metallic piping systems, but HDPE is fundamentally immune to this threat. As a dielectric material, it doesn't conduct electricity, making it indifferent to galvanic corrosion or stray electrical currents. Laboratory data, including results from ASTM G22, confirms HDPE's resistance to a wide spectrum of pH levels, aggressive soils, and saltwater.
Additionally, HDPE resists Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC), a phenomenon that eats away at ductile iron and steel pipes in sewage and raw water applications. In coastal industrial zones where saline groundwater attacks metal infrastructure, HDPE remains inert. This chemical resistance extends to strong acids and alkalis, making it suitable not just for potable water, but also for industrial process water where chemical runoff might destroy other materials.
Case Studies: Metal vs. HDPE Failure Rates
Field data backs this up. A comparative analysis of municipal water systems over a 15-year period shows a stark contrast in failure rates. Ductile iron pipes, even those with poly-wrap protection, often show pitting and graphitization within two decades in "hot" soils.
In contrast, HDPE pipes maintain their structural integrity indefinitely in the exact same conditions. Statistical data indicates the average annual failure rate for HDPE is approximately 0.3 per 100 km—significantly lower than metallic alternatives. A 2012 study highlighted that while ductile iron pipe failures jumped by 13% due to aging and corrosion, HDPE systems in the same network reported zero corrosion-related breaks, validating its use in aggressive geotechnical conditions.
Potable Water Safety and Inertness
For water supply authorities, water quality is non-negotiable. HDPE is an inert material that complies with the strictest global hygiene standards, including NSF/ANSI 61 and WRAS. Unlike cement-lined pipes which can leach lime, or older metal pipes that release lead or copper byproducts, HDPE imparts no taste, odor, or toxicity to the drinking water.
We achieve this inertness through high-purity resins free from plasticizers or phthalates. The material’s resistance to leaching ensures the water at the tap is as clean as the water leaving the treatment plant. For B2B buyers supplying municipal contracts, this certification is a must-have, and HDPE’s inherent chemical stability offers the easiest path to compliance.
Eliminating Coatings: Total Cost of Ownership
Metallic pipes come with hidden price tags in the form of protective measures. Specifying ductile iron or steel forces you to invest in expensive cathodic protection systems, polyethylene encasements, or internal epoxy linings. These additions spike your upfront capital expenditure and demand ongoing monitoring.
HDPE wipes these costs off the ledger. You don't need anodes, rectifiers, or protective wrappings. When calculating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over a 50-year horizon, the savings are massive. Eliminating corrosion mitigation can cut a project’s capital and operational budget by 40-45%, freeing up resources for system expansion rather than preservation.
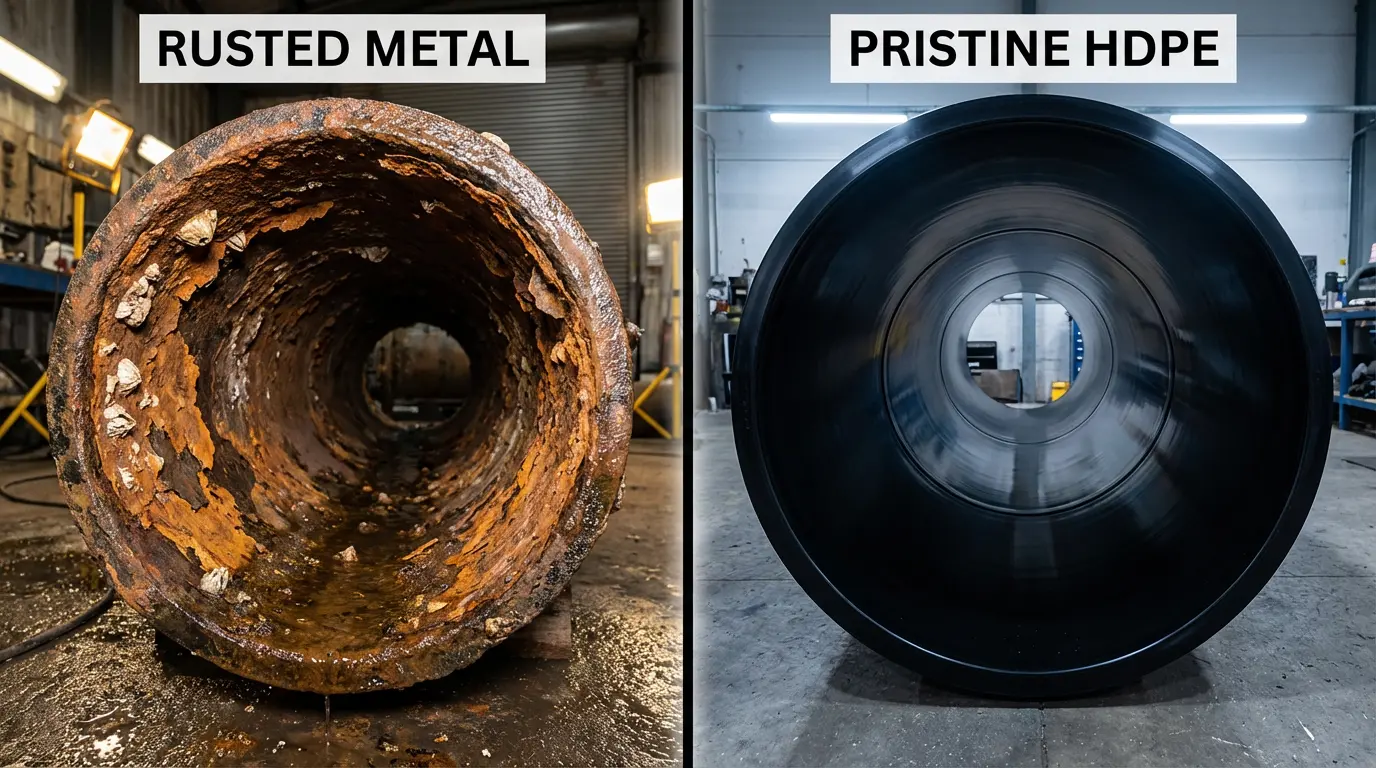

Corrosion comparison between metal pipe and HDPE water pipe
Core Advantage 2: Exceptional Leak-Free Joint Integrity
The Science of Fusion Joining
Traditional piping systems have a weak spot: the joint. Bell-and-spigot or gasketed connections are mechanical vulnerabilities prone to root intrusion and displacement. HDPE uses thermal fusion—specifically butt fusion and electrofusion—to create a system that is essentially one continuous pipe.
In butt fusion, pipe ends are faced, heated to a specific temperature, and pressed together under controlled pressure. This process causes the polymer chains to intermingle across the interface, cooling to form a monolithic joint. It’s not a "connection" in the traditional sense; it’s a homogenization of the material. The joint becomes as strong as, or often stronger than, the pipe itself, eliminating leak potential at connection points.
Pressure Testing and Joint Strength
You can verify the integrity of fused HDPE joints through rigorous testing standards like ASTM F2164. Hydrostatic pressure tests consistently show that when a fused pipe is pushed to burst pressure, failure occurs in the pipe body, not the joint. This proves the fusion process preserves the structural capability of the system.
For engineers, this reliability builds confidence in pressure ratings. Unlike PVC, where over-insertion or gasket rolling can lead to immediate or delayed leaks, a properly executed HDPE fusion joint is permanent. This reliability is critical for high-pressure transmission mains where a joint failure could result in catastrophic washouts.
Quantifying Water Loss Reduction
Non-Revenue Water (NRW) is a critical efficiency metric for water utilities. Switching to fused HDPE systems slashes these numbers. For instance, the city of Duluth, MN, reported a reduction in water loss from 16.5% to 11% shortly after beginning a strategic replacement of iron mains with HDPE.
On a broader scale, municipalities that have fully converted specific zones to welded HDPE systems have seen NRW drop below 5%—a figure virtually unattainable with gasketed joint systems. By eliminating mechanical gaskets that degrade over time, HDPE stops the "death by a thousand drips" that plagues aging infrastructure, preserving precious water resources and lowering treatment costs.
Field Efficiency of Fusion vs. Mechanical Connections
While fusion requires specialized equipment and trained technicians, the payoff in speed and reliability is huge for large-scale projects. Mechanical connections for metal pipes require thrust blocks at every turn to prevent joint separation under pressure. HDPE's fused joints are self-restraining, meaning you don't need concrete thrust blocking.
This speeds up installation in complex alignments significantly. An experienced fusion crew can produce reliable joints faster than a metal crew can bolt up flanges or pour thrust blocks. Plus, because the joints are self-restraining, the pipe can be assembled above ground and lowered into the trench in long strings. This minimizes the time trenches stay open and improves job site safety.
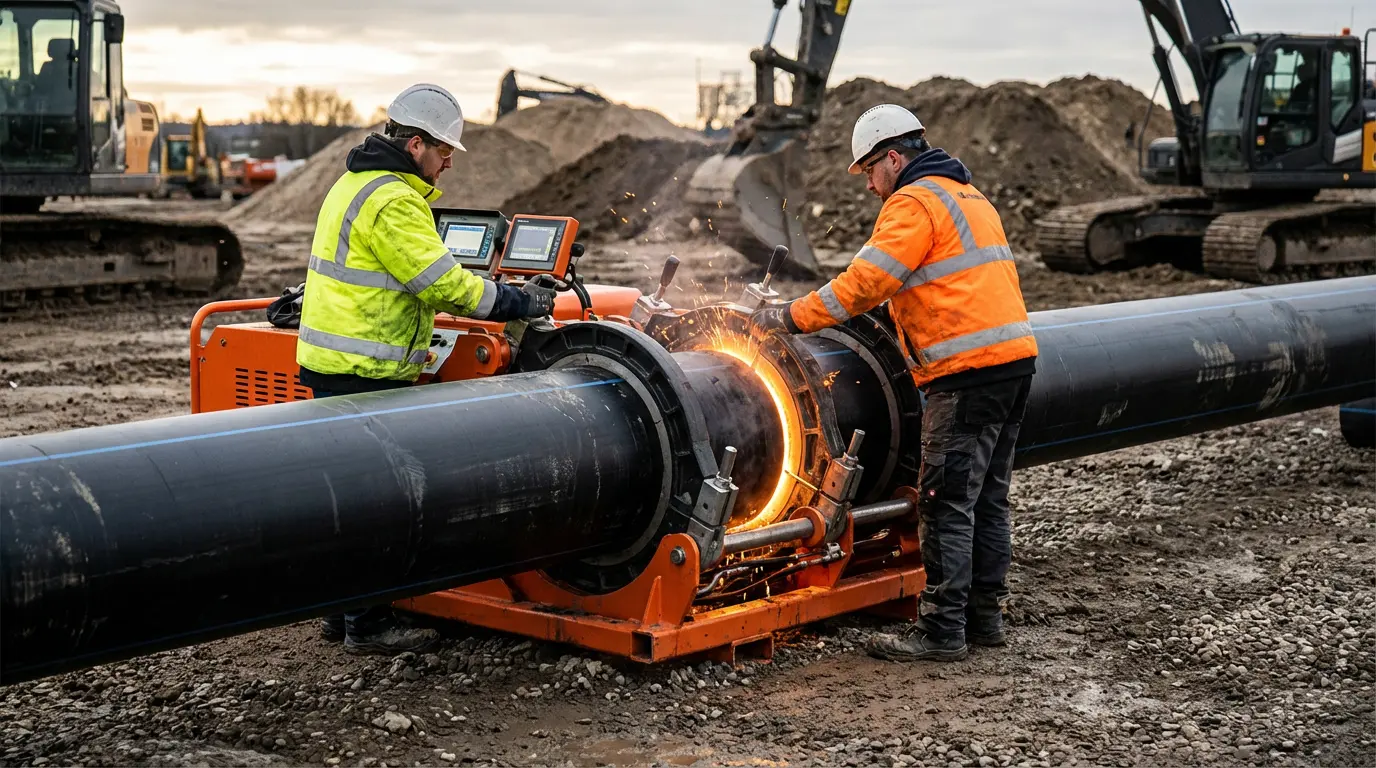

Butt fusion process of HDPE water pipes on construction site
Core Advantage 3: Superior Hydraulic Performance and Flow Efficiency
The Hazen-Williams Advantage
Pipe interior smoothness dictates flow efficiency, quantified by the Hazen-Williams 'C' factor. New HDPE pipe boasts a 'C' factor of 150-155, significantly higher than aged concrete (100-120) or corroded steel (which can drop to 80 or lower). A higher 'C' factor means less friction loss as water moves through the pipe.
For the system operator, this physics advantage hits the bottom line directly. Less friction means you can use smaller pumps or consume less energy to maintain the same flow rate. Over a pipeline's lifespan, electricity savings from reduced pumping head requirements can often offset the initial material cost entirely.
Maintaining Smooth Bore Over Time
The 'C' factor of metallic and cement-based pipes degrades over time due to tuberculation (corrosion buildup) and scaling. A steel pipe installed with a 'C' factor of 140 might drop to 100 within 20 years, drastically cutting its capacity.
HDPE water pipe maintains its smooth bore indefinitely. Its non-polar, anti-adhesive surface stops scale from bonding to the pipe wall. The hydraulic capacity you design at the start of the project remains consistent 50 years later. Engineers can design systems with tighter tolerances, knowing they don't need to over-size pumps to account for future friction increases.
Dampening Water Hammer
Water hammer—pressure surges caused by sudden changes in flow velocity—is a destructive force capable of bursting rigid pipes. HDPE's lower modulus of elasticity (flexibility) allows it to expand slightly to absorb these surge pressures.
Research indicates that for a given change in flow velocity, the surge pressure generated in HDPE is significantly lower than in steel or ductile iron. This repetitive shock absorption capability protects not only the pipe but also valuable inline equipment like valves and pumps. It effectively acts as a linear shock absorber, boosting the entire network's resilience against operational fluctuations.
Biofilm and Water Quality
Hydraulic smoothness isn't just about flow; it's about biological safety. The ultra-smooth interior of HDPE discourages biofilm adhesion—that slimy layer of bacteria that harbors pathogens. Rougher surfaces in concrete or pitted metal pipes provide ideal anchor points for microbial growth.
By inhibiting biofilm formation, HDPE reduces chlorine demand in the distribution system. Utilities can maintain residual disinfectant levels more easily, ensuring water safety at the furthest points of the network. This link between hydraulic surface quality and public health is a compelling argument for switching to HDPE in potable water applications.
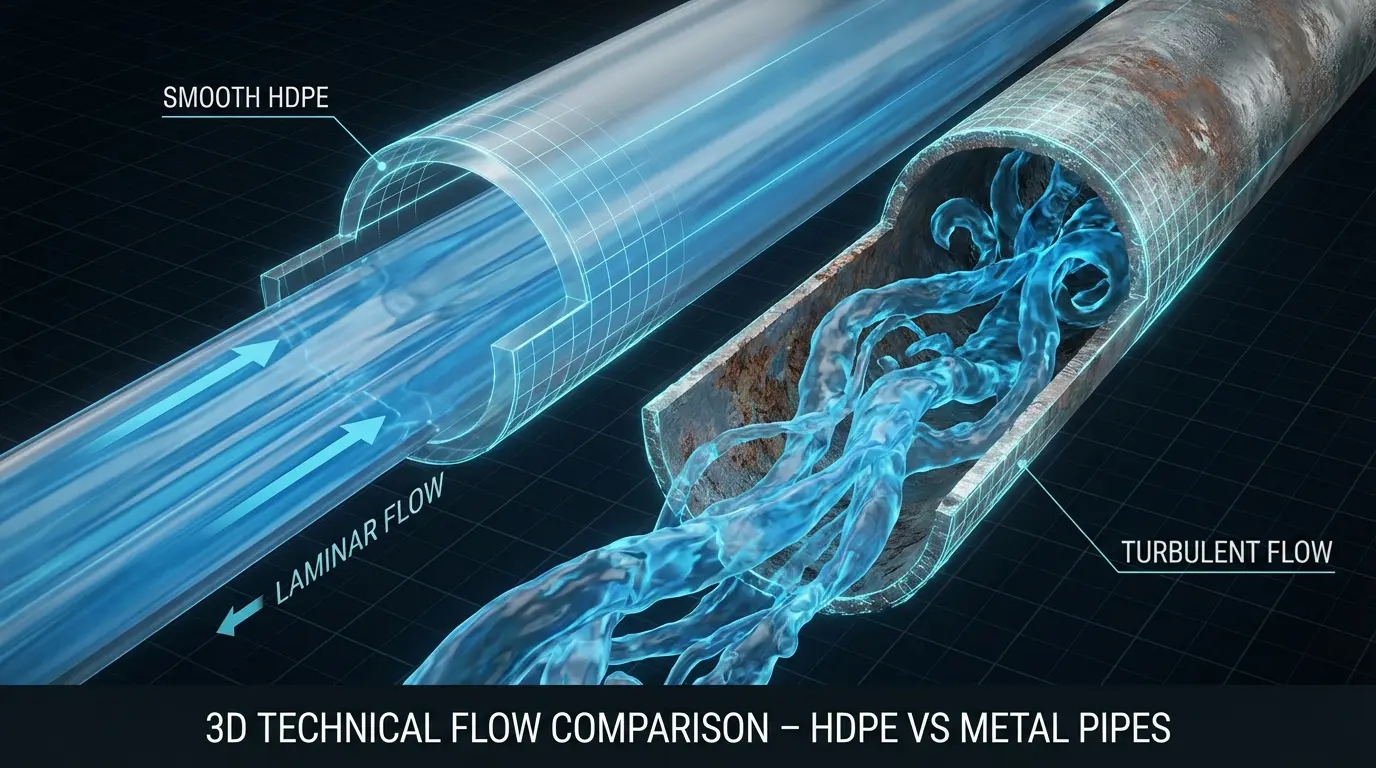
Hydraulic flow efficiency comparison diagram
Core Advantage 4: Outstanding Flexibility and Durability Under Stress
Seismic and Ground Movement Resilience
In geologically active regions, rigid pipes shear during earthquakes or ground settling. HDPE's high strain capacity allows it to structurally deform without cracking. Laboratory tests simulating seismic stress have subjected fused PE joints to 6% axial strain with zero damage.
This flexibility allows the pipe to snake through the ground, accommodating soil shifting, frost heave, and liquefaction. For B2B buyers in seismic zones like Japan, California, or Chile, HDPE is the standard for survivability. It moves *with* the ground rather than fighting against it, ensuring water supply continues even after significant seismic events.
Trenchless Installation Capabilities
HDPE’s flexibility is the key enabler for trenchless technologies like Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) and pipe bursting. These methods minimize surface disruption, saving roads and landscapes. HDPE's bend radius is impressive; a standard DR 11 pipe can be cold bent to a radius of 25 times its outer diameter.
This capability was highlighted in a Newton, MA project, where a 500mm HDPE pipe was pulled through a bore path to replace an aging main. Pulling long, continuous strings of pipe through underground bores reduces excavation costs and accelerates project timelines—advantages rigid pipes simply cannot offer.
Fatigue Resistance vs. PVC-M
Water distribution systems breathe; they are subject to cyclic pressure loading from pump cycles and demand fluctuations. Brittle materials like PVC-M are susceptible to fatigue failure, where microscopic cracks propagate over time.
HDPE behaves differently. It is a viscoelastic material highly resistant to fatigue. It can withstand millions of pressure cycles without a reduction in its hydrostatic design strength. This makes it particularly suitable for force mains and sewer rising mains where pressure surges are frequent and severe.
Design Life and Pressure Ratings
We establish the Hydrostatic Design Basis (HDB) for HDPE through long-term testing (ASTM D2837) to predict performance over 50 to 100 years. The material is rated to maintain its strength well beyond the typical 25-year service life of lesser materials.
This longevity isn't theoretical. Early generation HDPE pipes installed in the 1960s are still in service today. Modern PE100 resins offer even greater safety margins. When an engineer specifies HDPE, they are designing for the next century, providing a legacy of reliability few other materials can match.
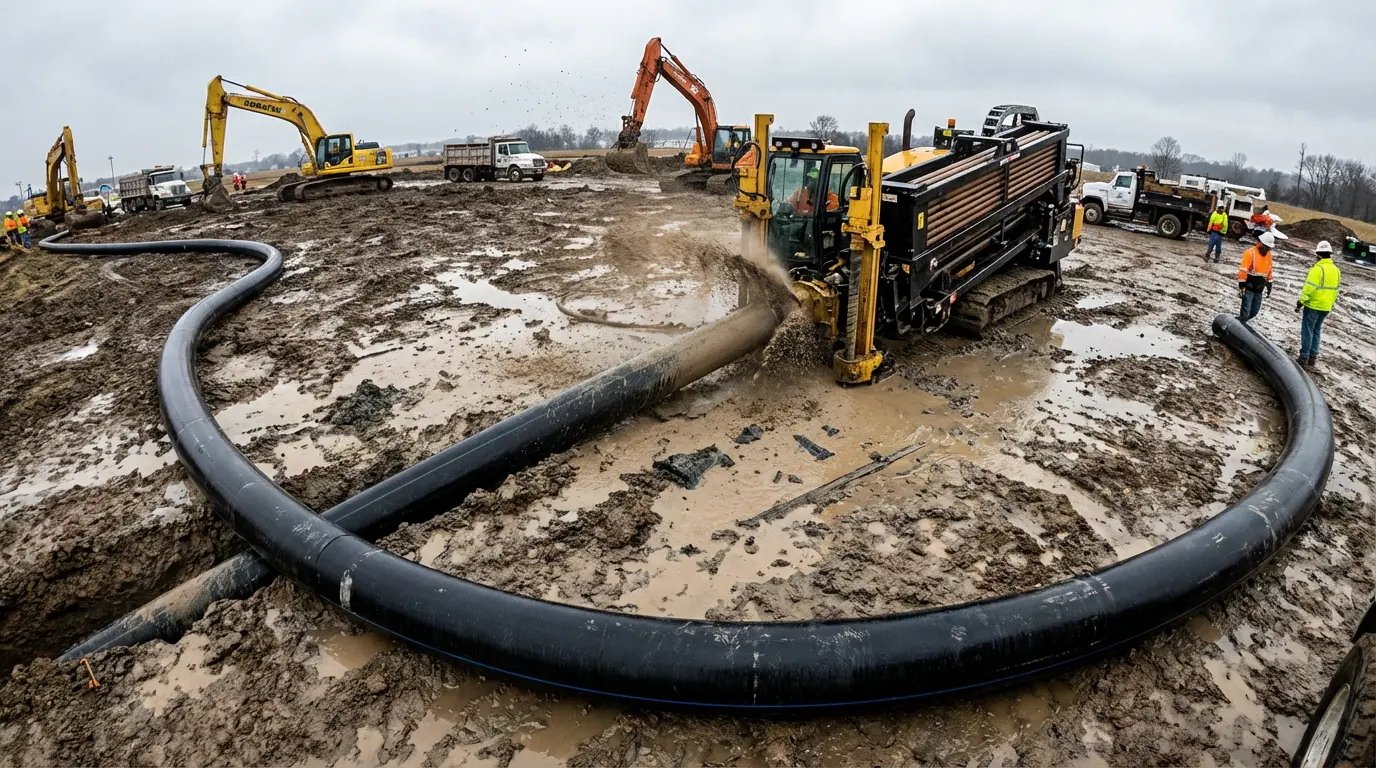

Trenchless HDD installation of HDPE pipe
Manufacturing Excellence & Quality Control
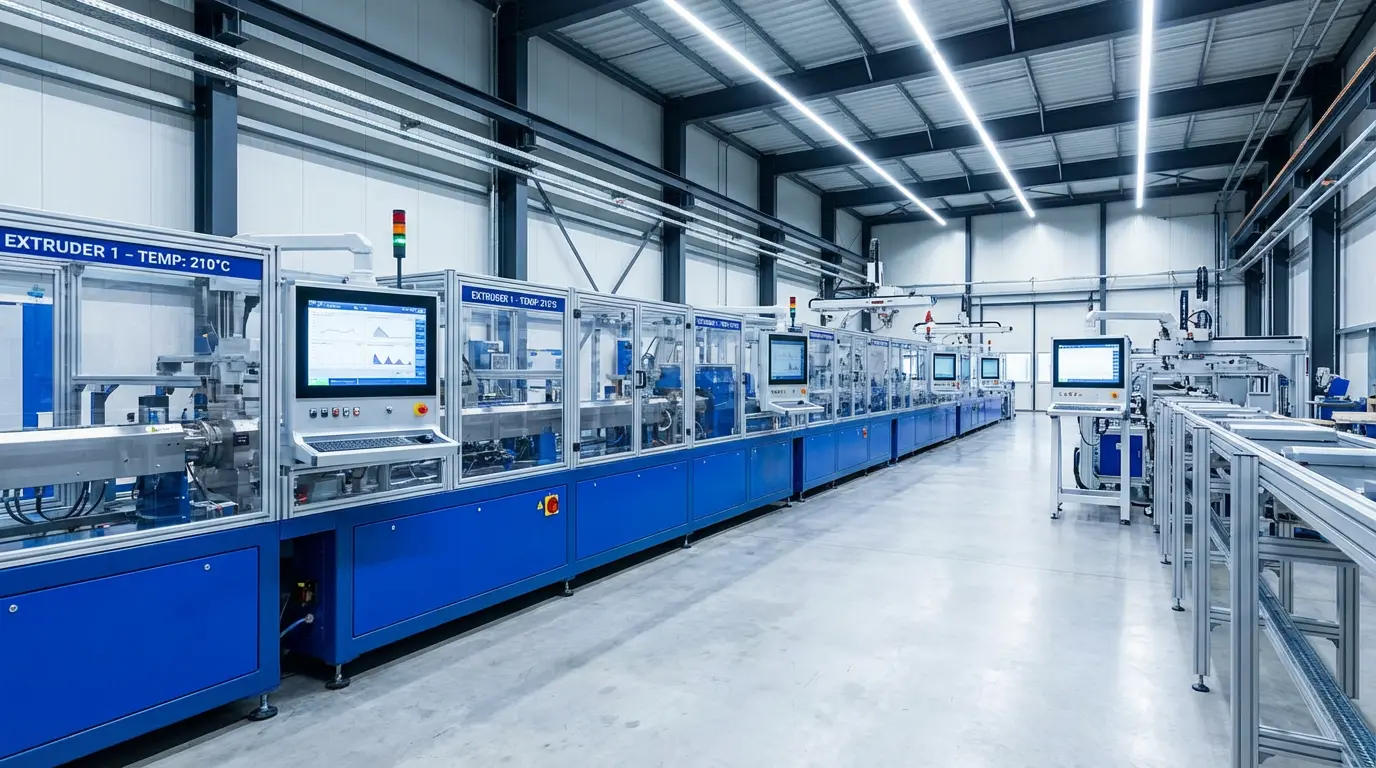
The Extrusion Process
Manufacturing top-tier HDPE water pipe is a game of precision. It begins with automated resin transport from silos to the extruder hopper. Inside the extruder, the resin is heated and sheared by a rotating screw. Computer controls monitor speed and temperature to ensure a homogeneous melt.
The molten polymer is pushed through a die to form the pipe shape, then pulled through a vacuum sizing tank to fix its dimensions. Cooling tanks gradually lower the temperature to prevent internal stresses. OEM factories utilize gravimetric feeding systems to precisely control weight per meter, ensuring wall thickness remains constant throughout the production run.
In-Line Quality Checks
Quality control isn't the final step; it’s integrated into the production line. Modern lines are equipped with ultrasonic thickness gauges that rotate around the pipe, measuring wall thickness and concentricity in real-time. Any deviation from the set tolerance triggers an immediate alarm and automatic adjustment.
Surface inspection systems scan for imperfections, scratches, or die lines. Ovality is constantly monitored to ensure the pipe remains perfectly round for easy joint fusion in the field. These automated systems ensure that every meter of pipe leaving the factory meets the strict dimensional requirements of ASTM D2122.
Critical Laboratory Testing
We don't just watch the line; we destroy samples in the lab to ensure the rest survive. The Hydrostatic Pressure Test (ASTM D1598) subjects pipe samples to elevated pressures at high temperatures to verify long-term strength. Notch tensile tests are conducted, particularly for PE100-RC grades, to confirm resistance to slow crack growth.
Melt Flow Index (MFI) tests ensure the resin's processing characteristics haven't degraded during extrusion. Carbon black content is verified (ASTM D1603) to guarantee UV protection. These rigorous protocols provide the data-backed assurance B2B buyers need when importing critical infrastructure components.
Plant Certifications
A reliable OEM partner must demonstrate systemic quality management. Look for factories certified to ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Product-specific certifications like WRAS (UK) or DVGW (Germany) indicate the manufacturer has passed stringent third-party audits. These marks are passports for global trade, assuring buyers that the pipe they receive is identical to the pipe that was tested.

HDPE pipe manufacturing extrusion line
Core Advantage 5: Cost-Effectiveness Across the Project Lifecycle
ROI and Installation Economics
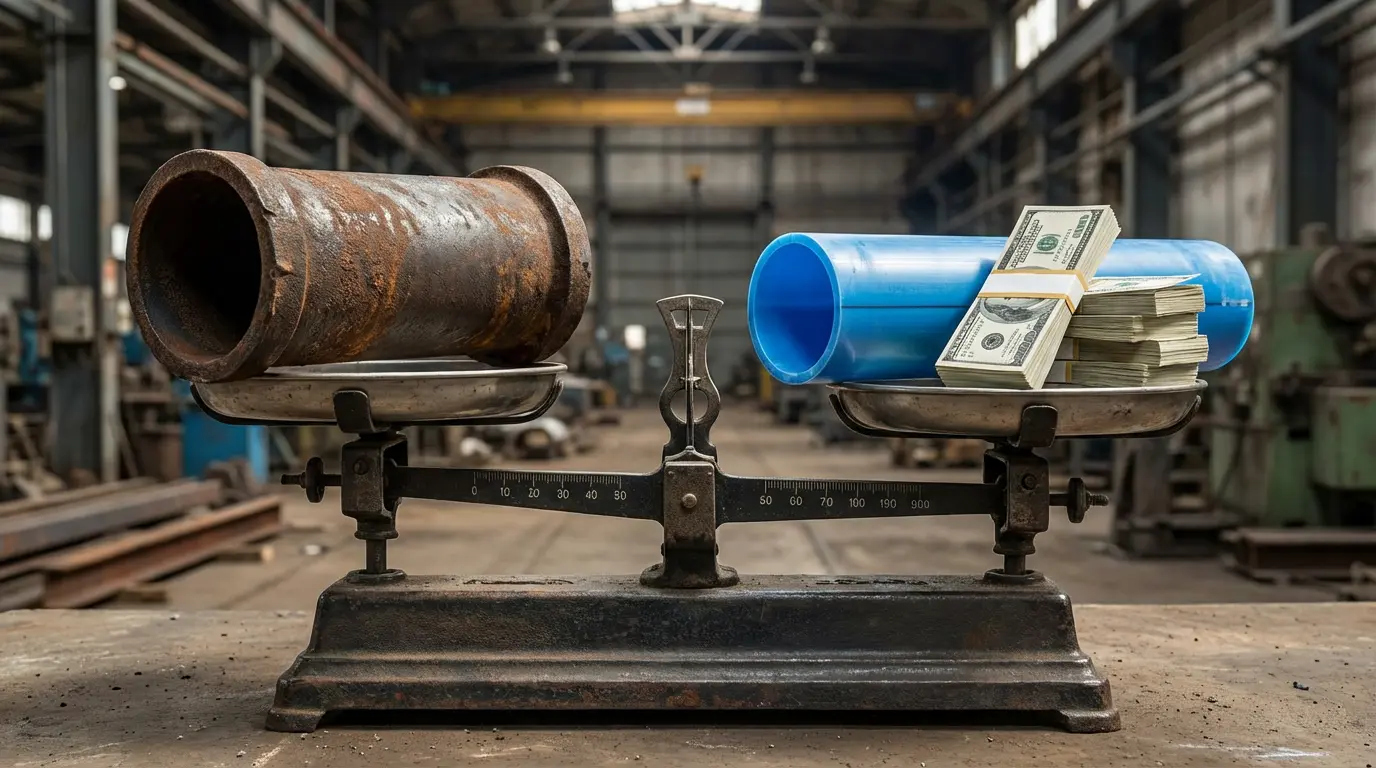
The sticker price per meter of HDPE might sometimes exceed PVC, but the installed cost often favors HDPE. An ROI model for a 5km, 300mm diameter water main reveals significant savings. Eliminating thrust blocks, reducing trench width (thanks to above-ground fusion), and faster installation combine to lower total civil works costs.
When compared against Ductile Iron, the savings are even more pronounced. HDPE is lightweight (approx. 1/8th the weight of steel), which drastically reduces transportation costs. A standard flatbed truck can carry significantly more HDPE pipe than concrete or iron, and on-site handling requires smaller, less expensive excavators, slashing the heavy machinery rental budget.
Long-Term O&M Savings
You realize the true value of HDPE water pipe during the Operational & Maintenance (O&M) phase. With a leak-free system, costs associated with repairing breaks, repaving roads after repairs, and compensating for water damage disappear.
Furthermore, the hydraulic efficiency discussed earlier leads to permanent energy savings. Municipal engineers utilizing lifecycle cost analysis (LCCA) consistently find that HDPE is the most economical choice over a 50-year period. There is no need for relining or rehabilitation budgets typically reserved for metallic pipes at the 20-30 year mark.
Asset Depreciation and Planning
For utility owners, asset depreciation is a key financial metric. The recognized design life of 50-100 years for HDPE allows utilities to depreciate the asset over a much longer period compared to materials with shorter lifespans. This improves the utility's financial health and justifies the initial capital investment to stakeholders and ratepayers.

Cost comparison weight and value of HDPE vs metal pipe
Core Advantage 6: Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Lower Embodied Carbon
In an era of green procurement, the carbon footprint of construction materials is under the microscope. HDPE performs exceptionally well here. The embodied energy required to manufacture, transport, and install HDPE pipe is significantly lower than traditional materials. Studies indicate that HDPE pipe has approximately 52% less embodied carbon than concrete or steel pipe of equivalent capacity.
The lower weight reduces fuel consumption during transport. Additionally, the lower melting point of polyethylene compared to the smelting temperatures of steel means less energy is consumed during the manufacturing phase.
Recyclability and Circular Economy
As a thermoplastic, HDPE can be melted and reformed repeatedly. Post-industrial scrap from the manufacturing process is 100% recyclable. Even at the end of its service life, HDPE piping can be recycled into non-pressure applications like drainage pipes or cable conduits.
The industry currently utilizes hundreds of millions of pounds of recycled resin annually. This recyclability supports the circular economy, reducing demand for virgin fossil fuels and minimizing construction waste sent to landfills.
Water Conservation (UN SDG 6)
Perhaps the most significant environmental contribution of HDPE is water conservation. By providing a leak-free solution, HDPE systems directly support UN Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). Preventing the loss of treated water reduces strain on freshwater sources and the energy used to treat and pump water that never reaches the consumer.
Environmental Safety
HDPE is non-toxic and environmentally benign. It does not release harmful chemicals into the surrounding soil or groundwater. In the event of a catastrophic external force causing a break, the material doesn't shatter into sharp fragments that could damage other utilities. Its safety profile makes it the ideal choice for eco-sensitive areas and sustainable city planning.

Eco-friendly HDPE pipe in nature
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the maximum pressure and temperature HDPE water pipes can handle continuously?
Answer: Standard HDPE pipes are typically rated for continuous operation at temperatures up to 60°C (140°F). Pressure ratings depend on the Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR), but PE100 pipes can handle nominal pressures up to 25 bar (approx. 360 psi) for water applications. For higher temperatures, you must de-rate pressure ratings according to ISO standards to ensure longevity.
Q2: How does the cost of HDPE pipe fusion equipment and operator training impact the initial project budget?
Answer: While there is an upfront cost for fusion machines and training, think of it as a one-time investment in speed and reliability. Rental options are widely available for specific projects. The cost is generally offset by eliminating expensive mechanical fittings and thrust blocks, plus the reduction in installation time compared to traditional bell-and-spigot methods.
Q3: Are HDPE pipes suitable for above-ground installations, and how are they protected from UV degradation?
Answer: Yes, HDPE is excellent for above-ground use. The pipes are manufactured with 2-3% finely dispersed carbon black, which acts as a powerful UV stabilizer. This allows the pipe to withstand direct sunlight for decades without becoming brittle or losing hydrostatic strength—unlike PVC, which requires painting or physical shielding.
Q4: What are the key differences between PE100 and PE100RC material grades, and when should I specify each?
Answer: Both grades share the same Minimum Required Strength (MRS). However, PE100-RC (Resistant to Crack) is engineered with higher stress crack resistance. PE100 is suitable for standard sand-bedded trenches. You should specify PE100-RC for trenchless applications (HDD) or installations using native soil backfill where rocks might create point loads on the pipe surface.
Conclusion
The shift toward HDPE water pipe isn't just an upgrade; it is a fundamental change in how we approach water infrastructure. By leveraging these six core advantages—unmatched corrosion resistance, leak-free fused joints, superior hydraulic efficiency, flexibility under stress, lifecycle cost savings, and environmental sustainability—engineers and buyers can finally solve the perennial problems of water loss and infrastructure decay.
HDPE is not just a pipe; it is a guarantee of performance for the next century. Whether you are replacing aging urban mains or installing new transmission lines in rugged terrain, HDPE offers the technical properties required to succeed.
Ready to specify or procure HDPE pipes for your next project? Contact our technical sales team today for a free project consultation, detailed technical datasheets, and samples to test against your specific requirements. We offer factory-direct pricing and full OEM customization to meet your exact specifications.

