Table of Contents
Introduction
For procurement officers, construction engineers, and project managers, the difference between a successful product rollout and a costly recall often lies in the microscopic details of the polymer matrix. While the global market is saturated with decorative and industrial material options, true value isn't found on the surface—it’s found in the engineering excellence behind the production line. A lack of insight into manufacturing standards can lead to sourcing materials that fail under tension, yellow with age, or lack the chemical resistance required for harsh industrial environments.
This guide pulls back the curtain on PVC film production. We will bypass generic definitions to examine the engineering nuances—from resin K-values to calendering nip pressures—that distinguish commodity plastic from high-performance industrial films.
Here, you will gain a technical, actionable understanding of the manufacturing process. Whether you are sourcing for furniture lamination, sterile medical packaging, or architectural membranes, understanding the science ensures you secure the durability and cost-efficiency your projects demand.

Understanding PVC Film: Properties, Types, and Applications
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) film is more than just a plastic sheet; it is a programmable thermoplastic solution. Created through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer, its value in the B2B sector comes from its adaptability. Manufacturers can engineer it to be as rigid as a pipe or as soft as fabric. Its indispensability relies on a unique triad of properties: chemical stability, exceptional tensile strength, and—in its plasticized form—superior flexibility.
Market Dynamics and Growth
The appetite for these materials shows no signs of slowing. 2024 market data values the global flexible PVC film sector alone at approximately USD 3.46 Billion. With a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.24%, the market is on track to hit USD 8.8 Billion by 2032. This surge is largely fueled by infrastructure booms in emerging economies and the critical need for sterile medical barriers.
Differentiating PVC Film Types
To specify the right material, one must understand the formulation differences:
- Rigid PVC Film (UPVC): These formulations contain little to no plasticizer. The result is a film with high modulus and stiffness, perfect for blister packaging, smart card overlays, and protective pipe wrapping. They excel in maintaining structural integrity under stress.
- Flexible PVC Film: The addition of plasticizers disrupts the intermolecular forces, allowing the chains to slide past one another. These are the workhorses for applications requiring drape and elasticity, such as flooring wear layers, wire insulation, and soft signage.
- Semi-Rigid Film: A hybrid approach, often deployed in decorative furniture foils where the material must conform to curves yet retain a hard, scratch-resistant surface.
From construction membranes capable of waterproofing commercial rooftops to automotive interiors demanding soft-touch skins, the applications are vast. In healthcare, high-purity films are non-negotiable for IV bags, requiring production environments that rival cleanrooms.

The Foundation: Raw Materials and Their Quality Control
High-performance film isn't made on the machine; it's born in the laboratory. The process starts with the rigorous selection of PVC Resin, typically suspension grade. For film extrusion and calendering, the K-value (indicating molecular weight) is the primary specification. We typically utilize resins with a K-value between 60 and 75 (grades SG-3 to SG-5). A higher K-value improves mechanical strength and surface finish but demands higher processing temperatures and torque.
The Role of Additives
Pure PVC is naturally brittle and thermally unstable. Additives are the chemistry that transforms raw resin into a functional product:
- Plasticizers: These dictate flexibility. The industry is pivoting toward safety and sustainability. We prioritize phthalate-free options like DOTP (Dioctyl terephthalate) and bio-based plasticizers, with some modern eco-formulations containing up to 25% bio-content.
- Heat Stabilizers: PVC degrades rapidly under heat. To prevent burning during processing, stabilizers are introduced. Calcium-Zinc (Ca-Zn) systems have largely ousted lead-based stabilizers in premium production to meet global safety standards, though Organotin remains in use for specific high-clarity rigid applications.
- Lubricants & Colorants: A precise balance of internal and external lubricants ensures the molten plastic flows smoothly without sticking to the metal calender rolls. High-grade pigments are added for color fastness and UV stability.
Incoming Quality Control
We maintain a "gatekeeper" policy for raw materials. Every batch of resin and additive faces purity analysis before entering the warehouse. We strictly adhere to MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) protocols and environmental frameworks like REACH and RoHS. This guarantees the final film is devoid of hazardous heavy metals—a mandatory requirement for export to European and North American markets.

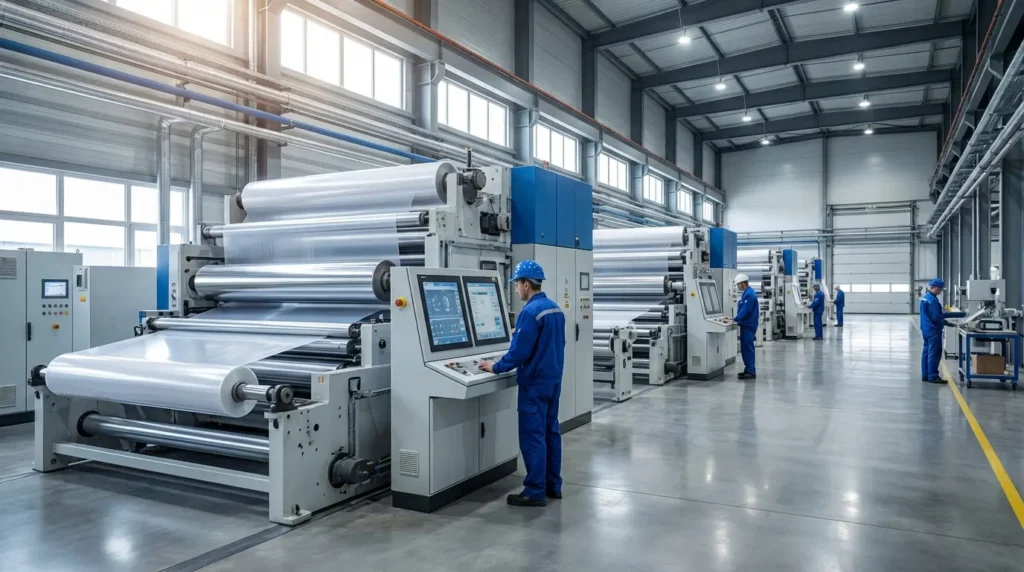
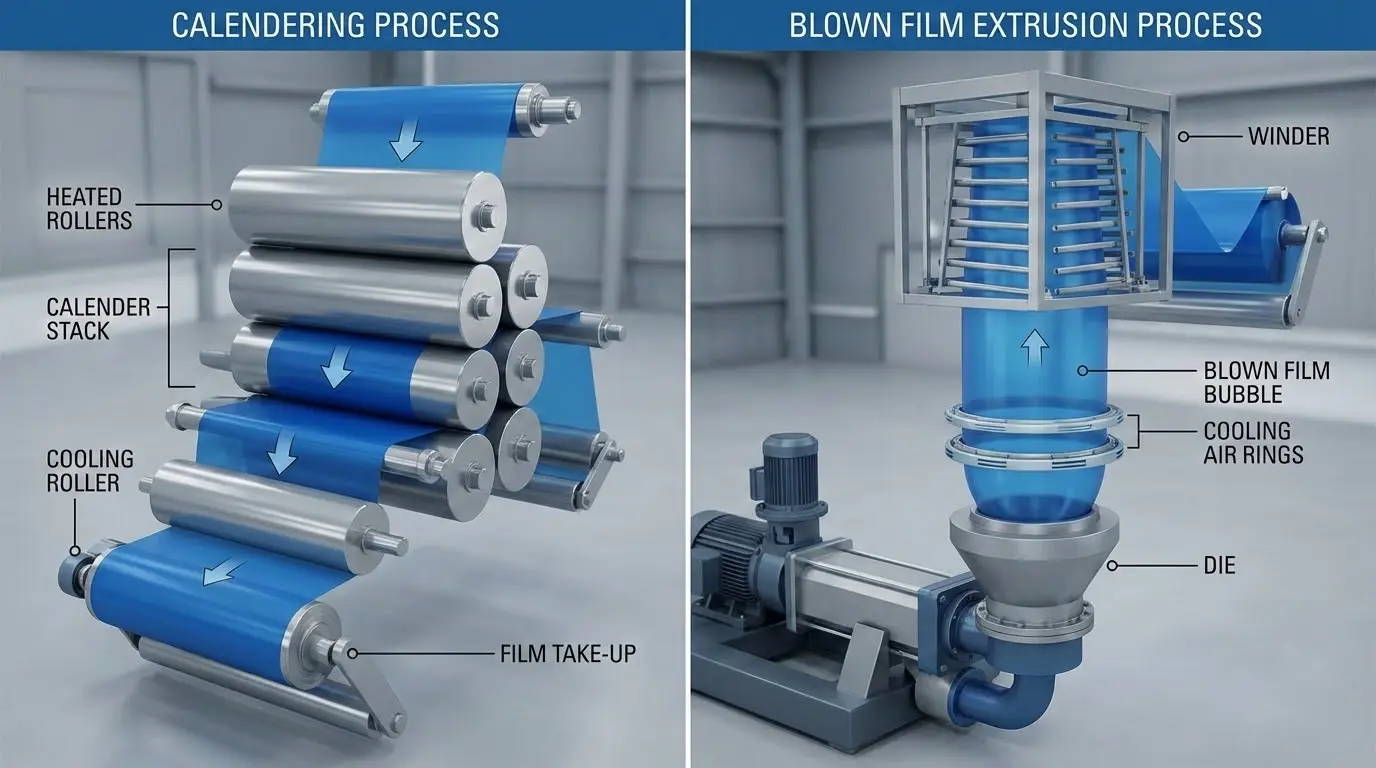
The Core Process: How PVC Film is Made (Calendering Method)
For high-volume, uniform production, Calendering is the industry standard. This mechanical process forces a molten mass of PVC between a series of counter-rotating heated rolls, squeezing it into a continuous, precise sheet.
1. Compounding and Mixing
Precision begins at the scale. Resin, plasticizers, and stabilizers are weighed and fed into a high-speed mixer. Friction from the mixing blades drives the temperature up to 110-120°C. This "dry-blending" phase allows the porous PVC grains to absorb the liquid plasticizers, creating a dry, free-flowing powder that is chemically homogeneous.
2. Gelation and Filtration
The dry blend moves to a planetary extruder or mixing mill, where shear force and heat (160–180°C, max 190°C) transform the powder into a molten, dough-like melt. Crucially, this melt is forced through a 200-mesh filter (pore size ≤75μm). This step captures any unmelted particles or contaminants, ensuring the final film is free of "fish eyes" or surface defects.
3. The Calendering Stack
The filtered melt enters the calender, usually a 4-roll machine in an inverted "L" or "Z" configuration. The material passes through the "nips" (gaps) between rolls. As it travels, it is thinned and widened.
- Temperature Control: Thermal management is vital. A typical setup employs a cooling gradient across the stripping rolls—80°C / 60°C / 50°C—to gradually set the film's molecular structure.
- Surface Finish: The texture is imparted by the final roll. A mirror-polished chrome roll yields high-gloss film, while a sandblasted roll creates a matte finish. For high-gloss output, our target surface roughness (Ra) is < 0.1μm.
4. Cooling and Winding
Leaving the hot rolls, the film is too soft to wind. It travels over cooling drums equipped with tension control to prevent shrinkage or deformation. Finally, the film is edge-trimmed (slitted) to the client's width and wound onto cores. Modern lines run at 6-40 m/min for standard films, with specialized high-speed lines hitting 150 m/min.

Alternative Production Methods: Extrusion and Solution Casting
While calendering dominates high-volume production, specific performance requirements dictate alternative methods.
Extrusion (Cast and Blown)
Cast Extrusion: The PVC melt is extruded through a flat T-die directly onto a chilled chrome roll. This is preferred for thinner films or when low internal stress is a priority.
Blown Film Extrusion: The polymer is extruded through a circular die and inflated with air to form a massive bubble. This process stretches the plastic in both the machine and transverse directions, significantly boosting mechanical strength. While less common for rigid PVC due to thermal sensitivity, it is the standard for cling films and specific packaging grades.
Solution Casting
When optical clarity is paramount, solution casting is the answer. PVC resin is dissolved in a solvent to form a liquid solution, which is then cast onto a moving belt. The solvent evaporates and is reclaimed. This method yields a film with isotropic properties (equal strength in all directions) and zero thermal stress history. However, it is slower and costlier, reserved for high-end medical or optical applications.
Comparison Summary
- Calendering: The champion of thickness uniformity and high volume.
- Extrusion: Cost-effective for smaller runs; blown film offers unique bi-axial strength.
- Casting: Unmatched clarity, but comes with a higher price tag.
Ensuring Excellence: Rigorous Quality Control and Testing
In the B2B supply chain, consistency builds trust. A PVC film that fails during downstream processing costs time, money, and reputation. Consequently, our quality control (QC) spans from the production floor to the testing lab.
In-Process Monitoring
Our lines utilize automated beta-ray or X-ray thickness gauges that continuously scan the moving web. These systems feed data back to the calender controls, adjusting the nip gap in real-time to hold thickness tolerances within microns. Simultaneously, high-speed camera systems scan for gels, carbon specks, or streaks, automatically mapping any defects.
Laboratory Verification
Post-production, we subject samples to destructive testing based on international standards:
- Tensile Strength & Elongation: Verified via ASTM D882. We ensure the film can bear loads and stretch without snapping—critical for vacuum forming.
- Tear Resistance: Measured via ASTM D1004. This simulates the film's ability to stop a rip from propagating once punctured.
- Chemical & Environmental Testing: Films are exposed to acids, bases, and UV radiation to predict longevity. Migration tests confirm that plasticizers remain stable and do not leach out.
Operating under ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems, we ensure every roll is fully traceable to its raw material batch and processing parameters.

Innovations and Sustainability in PVC Film Manufacturing
The PVC industry is undergoing a transformation. The "toxic plastic" narrative is being dismantled by high-tech, sustainable engineering.
Eco-Friendly Formulations
Sustainability begins with chemistry. We have aggressively transitioned to Calcium-Zinc (Ca-Zn) stabilizers, eliminating lead and cadmium from our facility entirely. Furthermore, adopting bio-based plasticizers derived from soy and renewable resources allows us to reduce fossil fuel reliance without sacrificing flexibility. Low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) formulations are now standard for indoor decorative films, ensuring healthy air quality for end-users.
Advanced Surface Treatments
Innovation extends to the surface. We employ Corona and Plasma treatments to modify surface energy, drastically improving ink adhesion for printing clients. Multi-layer co-extrusion technology enables us to engineer films with a recycled core and a virgin, high-performance outer skin—balancing cost-efficiency with premium aesthetics.
Energy Efficiency
Calendering is energy-intensive, but we are driving efficiency up. Our newest lines consume approximately 0.4 kWh/kg, setting a new efficiency benchmark. We also utilize closed-loop recycling systems; edge trims and startup waste are immediately reground and reintroduced into the mix, ensuring near-zero material waste.

Our Manufacturing Excellence & Quality Assurance: Your Trusted Partner
As a premier PVC Decorative Material & Industrial Pipe Factory, we view our product as a foundational component of your reputation. Our facility isn't just a factory; it is a hub of material science designed to support global B2B partners.
State-of-the-Art Capabilities
Our floor features automated mixing and calendering systems engineered for large-scale precision. We offer deep customization, from specific K-value resin selection to custom color matching and embossing. Whether you require rigid film for cooling tower fills or soft-touch skins for luxury packaging, our R&D team collaborates directly with your engineers to formulate the solution.
Unwavering Support
We believe in factory-direct transparency. Our partners benefit from direct access to technical data, transparent pricing that cuts out middleman markups, and a supply chain built for on-time delivery. Our quality assurance protocols, aligned with ISO 9001 and FDA compliance where applicable, mean you receive certified quality in every container.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the main difference between rigid and flexible PVC film?
The difference lies in the plasticizer. Rigid PVC (UPVC) has little to no plasticizer, resulting in a stiff, impact-resistant material used for packaging and cards. Flexible PVC contains plasticizers (like DOTP) that relax the polymer chains, creating a pliable material suitable for upholstery, flooring, and inflatables.
Q2: How do you ensure your PVC film is environmentally compliant?
We strictly adhere to REACH and RoHS regulations. Our films are free from heavy metals like lead and hazardous phthalates. We utilize Calcium-Zinc stabilizers and offer bio-based plasticizer options. Additionally, our closed-loop recycling process reclaims edge trims, minimizing waste and carbon footprint.
Q3: What quality certifications does your film meet?
Our manufacturing process is ISO 9001 certified. We test against international standards including ASTM D882 (tensile strength) and ASTM D1004 (tear resistance). For specific industries, we provide compliance data for food contact (FDA) or medical-grade requirements upon request.
Q4: Can you produce custom formulations for large industrial orders?
Absolutely. Customization is our strength. We tailor formulations (UV stability, fire retardancy, cold crack resistance), dimensions, and surface finishes (matte, gloss, embossed) to your exact specifications. Our R&D team specializes in developing bespoke solutions for large-scale OEM/ODM projects.
Conclusion
Mastering the production of PVC film is paramount for those seeking optimal material performance. From the precise selection of resins and eco-friendly plasticizers to advanced calendering techniques and stringent QC protocols, every step dictates the final product's reliability. In a market crowded with varying grades of quality, understanding these technical details is the only way to ensure you invest in materials that protect your brand's reputation.
Do not leave material sourcing to chance. Partner with a manufacturer committed to transparency and innovation. Contact us today for a free consultation regarding your project requirements, or to request samples of our high-performance PVC film. Let our factory-direct expertise drive your next project's success.

